

Should a problem occur with macOS during a restart, perhaps because a storage space on the SSD is defective and thus a system component is no longer intact, this will be recognised by the startup process since the seal will now be invalid. So macOS itself cannot be changed by any software that you install as a user. And snapshots cannot be changed, even by the system itself. For further security, these Macs also do not start directly from the system volume, but from a snapshot of the system.
This seal is stored either in the T2 chip of the newer Intel Macs or in the Secure Enclave of the Apple M1/M2.Įach component of the system is signed in hierarchical order, and any change to a component would also invalidate the seal that represents the top level. Since macOS Big Sur, macOS has its home on its own volume, which is both read-only and cryptographically signed and sealed (referred to as a Sealed System Volume). Liquid Web’s Heroic Support is always available to assist customers with this or any other issue.In the past it was helpful to reinstall the system if you wanted to correct some Mac problems, but today this solution doesn’t make as much sense. In this example when a domain attempts to send mail to it will attempt to send mail to first and if that attempt fails it will try to send to next. The lower the number the higher the priority. The only difference is how to interrupt the Answer Section.įor MX, mail records, the answer will also include the priority of the mail server.

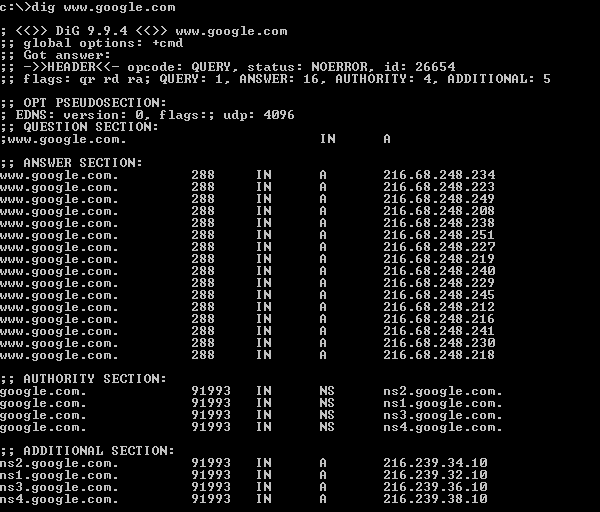
The result of an MX query is fairly close to the same as the result of a standard dig. flags: qr rd ra QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 2, AUTHORITY: 2, ADDITIONAL: 4 >HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 43051 Below is an example of the default output from a ‘ dig ‘: You probably don’t need all the information in the default output, but it’s probably worth knowing what it is. By default, however, dig is pretty verbose. Typically, the simplest query is for a single host. If you are using Windows you will need to install the BIND utilities package or any of the dig replacements that can be found by searching Google for Dig Windows. The dig command is a command that is used for querying DNS name servers for information about host addresses, mail exchanges, name servers, and related information.ĭig is included in most Linux and Mac OS X installations by default via the Terminal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
